Phenotyping Module - Overview
Phenotyping Module - Overview
The Phenotyping Module of T-Rx package aims to convert cleaned prescriptions (in long format) or prescribing episodes into ready-to-use treatment-related phenotypes (in wide format).
The Motivation
In (pharmaco-)epidemiological studies, prescription patterns are usually characterised/identified from prescriptions as proxy treatment phenotypes for downstream analysis.
Below are some examples in antidepressants:
- Treatment-resistant depression: publication
- Antidepressant switching: publication
The phenotyping algorithms are often described in publications, with codes embedded.
However, due to the complexity of prescription records and phenotyping algorithms, it is still challenging to apply codes for external academics.
This poses a huge challenge in scaling up analysis across datasets in (pharmaco-)epidemiological/genetic analyses.
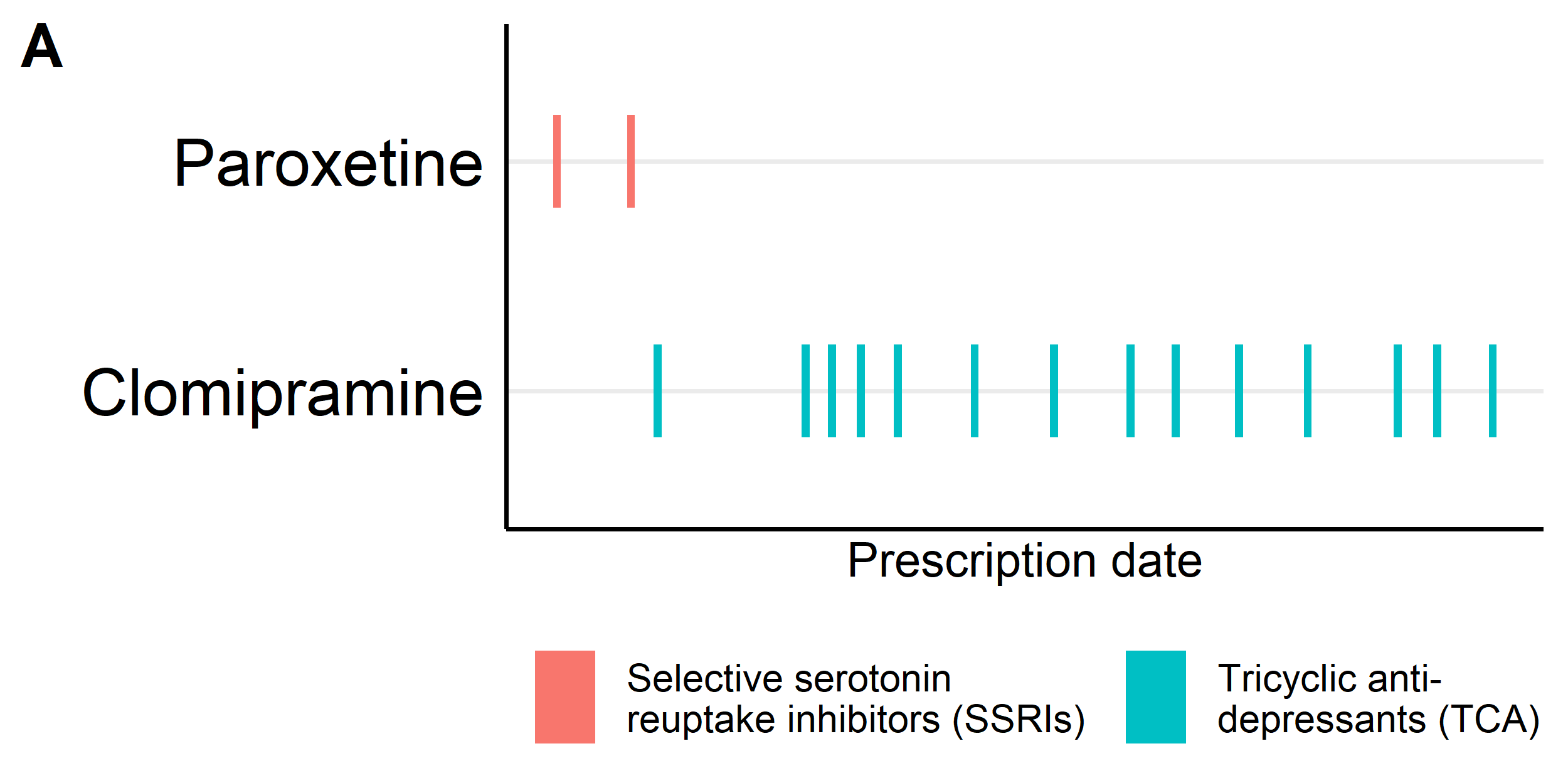
Figure 1: SSRI switching Illustration in UK Biobank
The Phenotyping Module
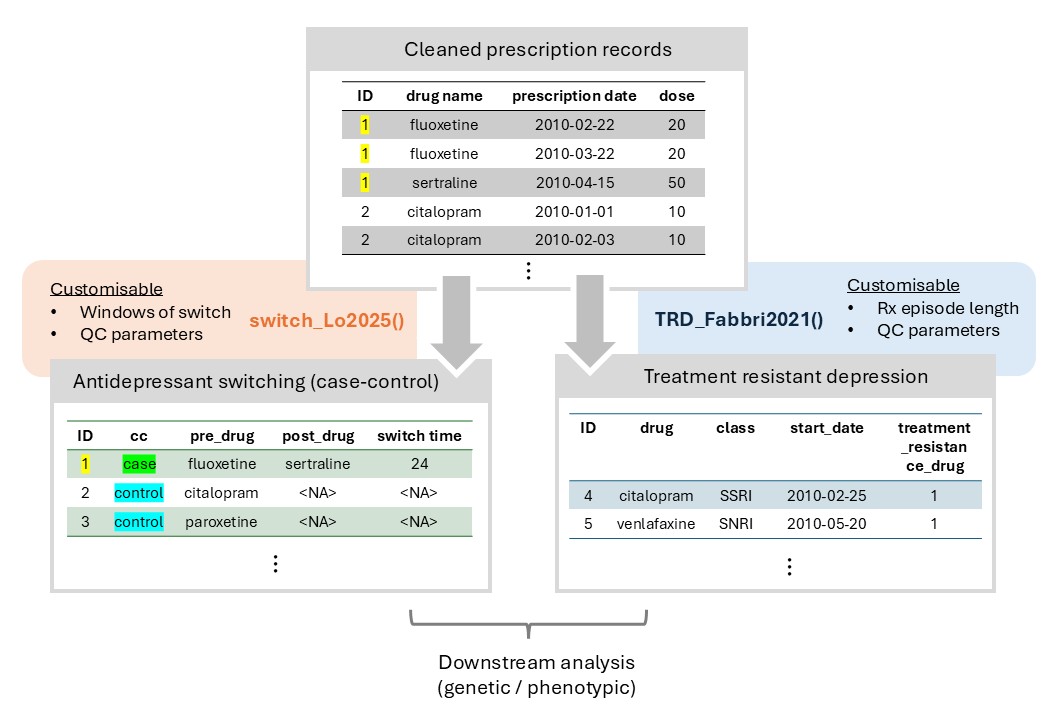
Figure 2: Overview of Phenotyping Module
With phenotyping module, users can provide prescription (as dataframe) and specify parameters as one-line R command, returning ready-to-analyse phenotypes and details.
To support open science, we also encourage academics to submit their published phenotyping algorithms (with scripts as functions, sample input and expected output).
Any questions?
Please post questions as an issue on the T-Rx GitHub repo here.
The T-Rx package is currently under beta testing. Most functions should have adequate documentation on possible errors.
Please kindly reach out to Chris Lo (chris.lowh@kcl.ac.uk) for feedback on documentation.
![]()